桥接(Bridge)是用于把抽象化与实现化解耦,使得二者可以独立变化。这种类型的设计模式属于结构型模式,它通过提供抽象化和实现化之间的桥接结构,来实现二者的解耦。
这种模式涉及到一个作为桥接的接口,使得实体类的功能独立于接口实现类。这两种类型的类可被结构化改变而互不影响。
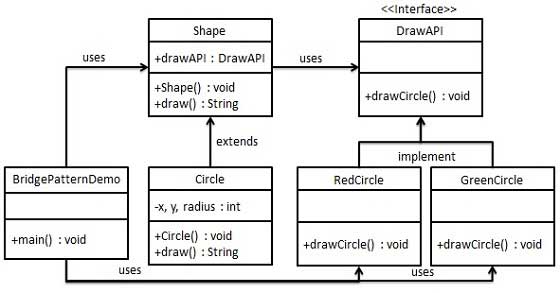
我们通过下面的实例来演示桥接模式(Bridge Pattern)的使用。其中,可以使用相同的抽象类方法但是不同的桥接实现类,来画出不同颜色的圆。
实现
我们有一个作为桥接实现的 DrawAPI 接口和实现了 DrawAPI 接口的实体类 RedCircle、GreenCircle。Shape 是一个抽象类,将使用 DrawAPI 的对象。BridgePatternDemo,我们的演示类使用 Shape 类来画出不同颜色的圆。
步骤 1
创建桥接实现接口。
DrawAPI.java
public interface DrawAPI {
public void drawCircle(int radius, int x, int y);
}
步骤 2
创建实现了 DrawAPI 接口的实体桥接实现类。
RedCircle.java
public class RedCircle implements DrawAPI {
@Override
public void drawCircle(int radius, int x, int y) {
System.out.println("Drawing Circle[ color: red, radius: "
+ radius +", x: " +x+", "+ y +"]");
}
}
GreenCircle.java
public class GreenCircle implements DrawAPI {
@Override
public void drawCircle(int radius, int x, int y) {
System.out.println("Drawing Circle[ color: green, radius: "
+ radius +", x: " +x+", "+ y +"]");
}
}
步骤 3
使用 DrawAPI 接口创建抽象类 Shape。
Shape.java
public abstract class Shape {
protected DrawAPI drawAPI;
protected Shape(DrawAPI drawAPI){
this.drawAPI = drawAPI;
}
public abstract void draw();
}
步骤 4
创建实现了 Shape 接口的实体类。
Circle.java
public class Circle extends Shape {
private int x, y, radius;
public Circle(int x, int y, int radius, DrawAPI drawAPI) {
super(drawAPI);
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.radius = radius;
}
public void draw() {
drawAPI.drawCircle(radius,x,y);
}
}
步骤 5
使用 Shape 和 DrawAPI 类画出不同颜色的圆。
BridgePatternDemo.java
public class BridgePatternDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Shape redCircle = new Circle(100,100, 10, new RedCircle());
Shape greenCircle = new Circle(100,100, 10, new GreenCircle());
redCircle.draw();
greenCircle.draw();
}
}
步骤 6
验证输出。
Drawing Circle[ color: red, radius: 10, x: 100, 100] Drawing Circle[ color: green, radius: 10, x: 100, 100]